Independent and Synergistic Associations Between TBI Characteristics and PTSD Symptom Clusters on Cognitive Performance and Postconcussive Symptoms in Iraq and Afghanistan Veterans
Abstract
Objective:
The investigators sought to evaluate the independent and interactive associations between mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) characteristics and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms with regard to postconcussive symptoms and cognition among treatment-seeking veterans of the U.S. conflicts in Iraq and Afghanistan.
Methods:
Sixty-seven Iraq and Afghanistan veterans who had a history of mTBI and comorbid PTSD were grouped based on injury mechanism (blast versus nonblast) and number of lifetime mTBIs (one to two versus three or more). Independent associations between mTBI characteristics and PTSD symptom clusters were evaluated with regard to cognition and postconcussive symptoms. Follow-up analyses were conducted to determine any interactive associations between TBI characteristics and PTSD symptom clusters.
Results:
Higher PTSD symptoms, particularly hyperarousal, were associated with poorer executive functioning and higher postconcussive symptoms. No direct relationships were observed between PTSD symptom clusters and memory or processing speed. The relationship between hyperarousal and processing speed was moderated by lifetime mTBIs, such that those with a history of at least three mTBIs demonstrated a negative association between hyperarousal and processing speed. Blast-related mTBI history was associated with reduced processing speed, compared with non-blast-related mTBI. However, an interaction was observed such that among those with blast-related mTBI history, higher re-experiencing symptoms were associated with poorer processing speed, whereas veterans without history of blast-related mTBI did not demonstrate an association between processing speed and re-experiencing symptoms.
Conclusions:
Higher hyperarousal and re-experiencing symptoms were associated with reduced processing speed among veterans with repetitive and blast-related mTBI history, respectively. PTSD symptoms, specifically hyperarousal, were associated with poorer executive functioning and higher postconcussive symptoms. Limited associations were found between injury characteristics and cognition chronically following mTBI. However, these results support synergistic effects of specific PTSD symptom clusters and TBI characteristics.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) occur at considerably high rates among veterans returning from the conflicts in Iraq and Afghanistan, with about 12%−20% of these veterans reporting an event consistent with mild TBI (mTBI) (1–4) and 23% being diagnosed with PTSD (5, 6). Notably, it may be more common to have both conditions than either disorder alone (7–9). Both mTBI and PTSD can result in subjective cognitive, emotional, and physical symptoms and objective cognitive difficulties that overlap and are often difficult to disentangle (10). The majority of studies evaluating clinical outcomes have found that subjective symptoms and objective neurocognitive deficits resolve within days or weeks following mTBI (11, 12). However, some studies have identified problematic symptoms and subtle cognitive difficulties months to years postinjury, especially in veteran samples (8, 13). These persisting symptoms are often related to mental health, psychosocial factors, and litigation status (14–16). Moreover, the combination of commonly co-occurring psychiatric disorders (PTSD, depression) with a history of military TBI places veterans at substantial risk for disability in occupational and social functioning (17).
Within the context of mTBI, certain injury characteristics (subsequently referred to as TBI characteristics), such as mechanism of injury and lifetime number of mTBIs, have been shown to play a role in both the maintenance of postconcussive symptoms and persisting cognitive deficits (18–20). Furthermore, symptoms of PTSD—particularly the type and severity of PTSD symptoms—have also been associated with long-lasting postconcussive symptoms and decrements in cognitive performance (21, 22). Moreover, greater mTBI injury burden in the context of PTSD has been associated with increased suicidal ideation (23, 24) and poorer functional outcomes (25) in the veteran population. This, taken together with evidence that cognitive difficulties predict reduced response to PTSD treatment (26, 27), suggests that a better understanding of independent and synergistic associations between TBI characteristics and PTSD symptom clusters in treatment-seeking veterans has the potential to inform treatment for veterans who served in Iraq and Afghanistan.
The literature regarding the association between TBI characteristics and persistent postconcussive symptoms and cognition across military and nonmilitary samples remains equivocal. In studies examining military samples, a history of multiple TBIs—particularly three or more mTBIs—has been associated with higher reporting of postconcussive symptoms (19, 28, 29) and reduced neurocognitive functioning and greater intraindividual variability on cognitive measures (19, 30), even when controlling for PTSD. In contrast, Cooper et al. (31) did not find differences on self-reported postconcussive symptoms or on a cognitive composite score between service members with mTBI histories and two groups without a history of TBI (history of orthopedic injury or PTSD). However, they identified a nonsignificant pattern of stepwise increases in subjective distress with increasing number of mTBIs.
In terms of mechanism of injury, the majority of studies evaluating military service members have compared those with a history of blast-related mTBI to those with mTBI from other mechanisms (e.g., blunt force) and have found largely similar postconcussive symptom reporting and neuropsychological performance across groups (18, 32–36). However, there is some evidence to suggest that a history of blast exposure—regardless of whether or not the exposure resulted in an mTBI—is associated with higher self-reported postconcussive symptoms (18, 37) and reduced executive functioning, processing speed, and verbal memory performance (38–40), although not all studies included PTSD as a covariate.
In addition to TBI characteristics, severity of PTSD symptoms has also been strongly associated with both self-reported postconcussive symptoms (35, 40) and objective neurocognitive functioning (41). In fact, PTSD along with other psychological and behavioral conditions has been demonstrated to have strong associations with neurobehavioral symptoms and cognitive dysfunction, whereas mTBI is only weakly related, particularly when taking these other factors into account (42, 43). More nuanced approaches have found that memory (44) as well as aspects of executive functioning, including response inhibition, suppression of distractors, and capture of attention may be particularly vulnerable to PTSD (45, 46). Although several studies have evaluated the influence of comorbid PTSD and a history of mTBI on cognition and postconcussive symptoms relative to either condition alone with mixed findings (47–50), the individual contributions of specific PTSD symptom clusters have been less frequently evaluated in veterans with PTSD and a history of mTBI. A better understanding of how specific symptom clusters of PTSD relate to outcomes may be particularly informative in monitoring and treating veterans with subthreshold PTSD, primarily those who endorse clinically meaningful symptoms in certain, but not necessarily all, cluster domains. In fact, some previous work suggests that poor outcomes, including neurocognitive dysfunction in certain domains, may depend on the particular profile of symptoms observed (21, 51).
In one study of 40 Iraq and Afghanistan veterans with PTSD (N=30 with a history of mTBI), Swick et al. (52) identified a positive association between impaired response inhibition and all PTSD symptom clusters on the PTSD Symptom Checklist (PCL) using the DSM-IV three-factor model (re-experiencing, avoidance/emotional numbing, and hyperarousal), with the strongest relationship being with re-experiencing symptoms. However, they did not include measures of other cognitive domains or a measure of performance validity, factors that are important to address in this population (53, 54). Another study evaluating the three-factor model of the PCL in veterans found significant associations between the hyperarousal cluster and postconcussive symptoms when removing postconcussive symptoms that overlap with PTSD or depression, but they did not include measures of objective cognitive functioning (22).
A four-factor model of PTSD symptoms that splits avoidance and numbing symptoms into two separate factors was found to improve fit over the original DSM-IV three-factor model (55), including in veterans with mTBI or close-range blast exposure history (56). In the only known study to evaluate the four-factor model of PTSD in relation to objective cognition among Iraq and Afghanistan veterans with and without PTSD, poorer visual memory performance was associated with higher PTSD symptoms in all clusters, and poorer verbal learning was associated with higher avoidance and numbing symptoms (21). Aase et al. (21) used only a single measure to assess cognition in each domain, however, and did not include a measure of self-reported postconcussive symptoms.
Although there is preliminary support for the proposal that TBI characteristics and greater severity of PTSD symptoms in certain clusters may confer additional risk for poor outcome following mTBI, no studies to date have examined possible synergistic effects on self-reported postconcussive symptoms and objective measures of cognitive performance. Additionally, there is a large body of literature suggesting that symptom overreporting and performance below expectations on cognitive validity measures are significant issues in this population (53, 54). This is particularly an issue within clinical settings (57), but can occur even in research contexts (58). However, not all studies referenced above have adequately accounted for these factors. The present study sought to evaluate the associations between TBI characteristics and PTSD symptom clusters on postconcussive symptoms and cognition (memory, processing speed, and executive functioning), as well as the interaction between TBI characteristics and PTSD symptom clusters, in treatment-seeking Iraq and Afghanistan veterans. Veterans with performance below expectations on performance and symptom validity measures were excluded from the study to reduce the influence of overreporting of clinical symptoms and invalid cognitive data.
First, we hypothesized that repetitive and blast-related mTBI would be associated with poorer cognitive performance and higher self-reported postconcussive symptoms (19, 29, 38–41). Second, given the nascent research into PTSD symptom clusters and the varying models of PTSD factor structure across studies, the analyses regarding relationships between specific PTSD symptom clusters and cognition/postconcussive symptoms were exploratory in nature and no specific hypotheses were generated. Third, we hypothesized that TBI characteristics would moderate the relationship between PTSD symptom clusters and cognition/postconcussive symptoms such that in those with repetitive and blast-related mTBI, higher PTSD symptoms across clusters would be associated with poorer cognition and higher postconcussive symptoms.
Methods
Participants and Procedure
Participants were Iraq and Afghanistan veterans with a history of mTBI, a current PTSD diagnosis, and self-reported cognitive complaints who were given a comprehensive neuropsychological assessment at baseline as part of a treatment study described previously (53, 59). For the purpose of the present study, mTBI was defined as self-reported loss of consciousness ≤30 minutes, alteration of consciousness up to 24 hours, and/or posttraumatic amnesia less than or equal to 24 hours, according to the VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for Management of Concussion/Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (60, 61). Current PTSD diagnosis based on DSM-IV criteria was confirmed by either a chart review of a diagnostic clinical interview conducted by a mental health professional or the administration of a structured diagnostic clinical interview (the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-IV), as has been done in previous studies (27, 59, 62).
A total of 100 participants were enrolled in the parent study and attended the baseline neuropsychological assessment appointment. The following exclusion criteria for the present study were assessed using medical chart review of diagnostic clinical interviews conducted by mental health professionals and detailed screening questions of the presence of psychiatric disorders: active alcohol or substance dependence defined by DSM-IV criteria (63); suicidal intent or attempt within the previous month; current psychotic disorder; Wide Range Achievement Test–Fourth Edition (64) (WRAT-4); Reading subtest standard score <75 (due to the possibility of a learning disorder); performance below standard cutoffs on performance validity measures; a score ≥33 on the Validity-10 (65), an embedded symptom validity measure within the Neurobehavioral Symptom Inventory (66) (NSI); a history of moderate or severe TBI; and missing more than one cognitive measure from a cognitive composite domain. For the present study, 33 veterans were excluded from the sample of 100 due to WRAT-4 Reading standard score below 75 (N=2), missing more than one cognitive measure from a cognitive composite domain (N=2), history of moderate TBI (N=6), and performance below expected cutoffs on any of the three performance validity measures described below or above a score of 33 on the embedded symptom validity measure described above (N=25). A total of 67 veterans were included in the present study (two veterans fell into two of these exclusion categories).
All procedures were approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System (VASDHS), and all participants provided written informed consent. Participants were veterans enrolled in Veterans Affairs services and subsequently enrolled in the parent treatment study (i.e., treatment-seeking veterans) and were recruited through advertisements and informational sessions at various clinics within the VASDHS, as well as veteran centers at local colleges.
TBI Diagnosis and Postconcussive Symptoms
The Warrior Administered Retrospective Casualty Assessment Tool (67) is a structured interview that was used to collect standardized information regarding participants’ TBI history. This measure gathers information about the number of TBIs, presence/duration of loss of consciousness and posttraumatic amnesia, and the mechanism of injury for each TBI. Consistent with the methodology of several previous publications, the number of lifetime TBIs was dichotomized into one to two prior mTBIs versus three or more (19, 28–30). Postconcussive symptoms were assessed using the NSI, a 22-item self-report measure that assesses symptoms occurring over the past 2 weeks on a Likert-type scale.
PTSD Symptomatology
PTSD symptomatology was assessed using the PTSD Checklist–Specific Trauma (68) (PCL-S). The PCL-S is a self-report measure that prompts respondents to rate how much they were bothered by all 17 DSM-IV items of PTSD (63) in the past month. Items are rated on a Likert-type scale ranging from 1 (not at all) to 5 (extremely). A total score can be obtained by adding all 17 items (range, 17–85), and it has been demonstrated to have a four-factor structure: re-experiencing, avoidance, hyperarousal, and numbing symptoms (56, 69, 70).
Neuropsychological Tests
Performance validity was assessed using the Test of Memory Malingering Trial 2 and Retention Trial (71) and the California Verbal Learning Test–Second Edition (CVLT-II) Forced Choice trial (72). Failure (as determined by standard published cutoffs in the manuals) on even one of these tests warrants consideration of poor performance validity among Iraq and Afghanistan veterans with a history of mTBI (73).
Because our hypotheses were specifically related to the neuropsychological domains of verbal memory, processing speed, and executive functioning, the following measures were selected from a larger battery for their sensitivity to impairments commonly observed in those with a history of mTBI and PTSD (74, 75). CVLT-II List A 1–5 Total Recall, Short Delay Free Recall, and Long Delay Free Recall measures were used for memory (72). In the domain of processing speed, the Symbol Search and Coding subtests were used from the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale–Fourth Edition (76) (WAIS-IV); subtests from the Color Word Interference Test (Color Naming and Word Reading) and Trail-Making Test (Visual Scanning, Number Sequencing, Letter Sequencing, and Motor Speed) were used from the Delis-Kaplan Executive Function System (D-KEFS) (77). With regard to executive functioning, subtests were used from the D-KEFS Color Word Interference Test (Inhibition and Inhibition Switching) and D-KEFS Trail-Making Test (Number-Letter Switching), as well as perseverative responses and errors, nonperseverative errors, and total errors from the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test–64 Card Version (WCST-64) (78). Finally, the WRAT-4 Reading subtest standard score was used as a measure of premorbid intellectual functioning.
In order to reduce the likelihood of type I errors and limit the number of analyses, cognitive composite scores were created. For the measures in which higher raw scores indicate worse performance (all Color Word, Trail-Making, and WCST scores), the raw scores were inverted and then converted into standardized z scores. For the measures in which higher raw scores indicated better performance, raw scores were converted directly into standardized z scores. Scores from each domain were then averaged to create three composite scores with higher z scores indicating better performance. Cronbach’s alpha was 0.90 for the memory composite, 0.89 for the processing speed composite, and 0.79 for the executive functioning composite, indicating high internal consistency for each composite. The intercorrelations between the composites ranged from r=0.24 to r=0.41.
Data Analysis
Because raw data for cognitive variables were used in all analyses, associations between cognitive composites and demographic variables (age, education, gender, WRAT reading score) were assessed, and any variables significantly related to cognitive performance were included as covariates in all analyses with that outcome variable. To examine associations between TBI characteristics and cognitive performance/self-reported postconcussive symptoms (aim 1), independent samples t tests were conducted with each of the three cognitive composite scores and the NSI total score as dependent variables and mechanism of injury (blast versus nonblast) or lifetime number of mTBIs (≥3 versus <3) as independent variables. To examine relationships between PTSD symptoms and cognitive performance/postconcussive symptoms (aim 2), Pearson correlations were used to identify significant associations between study variables. For any significant associations between the PCL-S total score and cognitive composites or the NSI, all four PTSD symptom clusters (re-experiencing, avoidance, hyperarousal, and numbing) were then entered as independent variables into a regression analysis predicting the cognitive composite score and/or NSI. Finally, to assess interactive relationships (aim 3), interaction terms were created using TBI characteristics and PTSD symptom clusters found to be associated with objective cognition or postconcussive symptoms to determine whether TBI characteristics moderated relationships between PTSD symptom clusters and cognition/postconcussive symptoms. It was determined a priori that although applying a more conservative p value would reduce the probability of type I error, these corrections were considered too stringent, given the relatively small sample size. As a result, we chose to use a more liberal criterion of p<0.05 to determine significance, in congruence with recommendations by Rothman (79). In short, Rothman argued that controlling for multiple comparisons can lead to errors in interpretation when using actual data versus random numbers and prevent findings from being published that warrant future replication and exploration. Effect sizes are provided to aid in interpretation.
Results
On average, veterans in the present sample had a mean age of 34.76 years (SD=8.15), with 13.79 (SD=1.98) years of education. Regarding deployment history, 28% were deployed once, 36% were deployed twice, 15% were deployed three times, and 15% were deployed four or more times. Approximately half of the sample (51%) had three or more lifetime mTBIs; the majority of veterans (63%) experienced at least one blast-related mTBI in their lifetime. Of those with three or more lifetime mTBIs, 22 had a history of blast-related mTBI and 12 did not. All veterans were in the postacute phase following their most recent mTBI (mean years postinjury=5.22 [SD=3.65]). On average, veterans reported a moderate level of depressive symptoms and difficulties involving sleep and pain. Complete descriptive statistics of the demographic, injury, and mental health variables are presented in Table 1.
| Variable | % | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 34.76 | 8.15 | |
| Male | 89.6 | ||
| Education (years) | 13.79 | 1.98 | |
| WRAT–4 reading standard score | 98.28 | 8.93 | |
| Ethnicity | |||
| Hispanic | 23.9 | ||
| White | 49.3 | ||
| African American | 16.4 | ||
| Asian | 6.0 | ||
| Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander | 1.5 | ||
| Other | 3.0 | ||
| Number of combat deploymentsb | |||
| 1 | 28.4 | ||
| 2 | 35.8 | ||
| 3 | 14.9 | ||
| ≥4 | 14.9 | ||
| Injury variables | |||
| Lifetime mTBIs | 2.99 | 2.06 | |
| ≥3 lifetime mTBIs | 50.7 | ||
| Blast history | 62.7 | ||
| Loss of consciousness history | 70.1 | ||
| Loss of consciousness duration, minutesc | 2.75 | 4.99 | |
| Posttraumatic amnesia history | 80.6 | ||
| Time since injury (years) | 5.22 | 3.65 | |
| Mental health variables | |||
| PCL-S total score | 57.76 | 10.57 | |
| NSI total score | 44.01 | 14.13 | |
| BDI-II total score | 26.43 | 10.27 | |
| BPI pain severity score | 4.57 | 1.76 | |
| BPI pain interference score | 4.86 | 2.53 | |
| PSQI global scored | 13.92 | 3.97 |
TABLE 1. Demographic characteristics and injury and psychiatric measures among Iraq and Afghanistan veterans (N=67)a
Prior to the main analyses, preliminary analyses tested for significant demographic (gender, age, education, WRAT reading standard score) predictors of outcome variables (Table 2). Age was negatively associated with the executive function composite (r=−0.33, df=65, p=0.006). Thus, age was included as a covariate in all analyses in which the executive function composite was the dependent variable. No other significant associations were observed between demographic variables and cognitive composites or postconcussive symptoms (all p values >0.05).
| Variable | Verbal memory | Processing speed | Executive functioningb | NSI total score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | –0.05 | –0.21 | –0.33* | –0.06 |
| Education | –0.08 | 0.02 | –0.10 | –0.02 |
| WRAT–4 reading score | –0.04 | –0.14 | 0.09 | 0.14 |
| PCL-S total score | –0.06 | –0.05 | –0.38* | 0.46* |
TABLE 2. Correlations between study variablesa
Association Between TBI Characteristics and Cognitive Performance/Postconcussive Symptoms
With regard to cognition, veterans with a history of blast-related mTBI performed worse on the processing speed composite (t=2.95, df=65, p=0.004), but not on the memory (t=−0.96, df=65, p=0.340) or executive functioning composites (F=0.70, df=1, 64, p=0.407) compared with those without a history of blast-related TBI. As for the relationship between number of mTBIs and cognition, the cognitive composites—memory, processing speed, and executive functioning—did not differ between those with one to two versus three or more lifetime mTBIs (all p values >0.05).
With respect to postconcussive symptoms, veterans with or without a history of blast-related mTBI did not differ on the NSI total score. Similarly, veterans with one to two versus three or more lifetime mTBIs did not differ on the NSI total score (all p values >0.05).
Association Between PTSD Symptom Clusters and Cognitive Performance/Postconcussive Symptoms
As shown in Table 2, the executive functioning composite was the only cognitive composite significantly associated with the PCL-S total score, such that higher PTSD symptoms were associated with poorer executive functioning performance when controlling for age. Thus, the four PTSD symptom clusters were entered into linear regressions with the executive functioning composite as the dependent variable, controlling for age. Full statistics for the regression analyses are shown in Table 3. Hyperarousal was the only PTSD symptom cluster that was significantly related to executive functioning (β=−0.37, p=0.025; all other p values >0.05).
| Executive functioninga | Neurobehavioral Symptom Inventorya | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | B | p | B | p |
| Age (years) | –0.430 | <0.001* | – | – |
| Re-experiencing | 0.155 | 0.294 | 0.076 | 0.611 |
| Avoidance | –0.079 | 0.517 | –0.112 | 0.361 |
| Hyperarousal | –0.368 | 0.025* | 0.460 | 0.005* |
| Numbing | –0.193 | 0.122 | 0.088 | 0.481 |
TABLE 3. Regressions with PTSD Checklist symptom clusters and executive functioning and postconcussive symptoms among Iraq and Afghanistan veterans
Postconcussive symptoms (as measured by the NSI total score) were significantly and positively correlated with the PCL-S total score (Table 2). When the four PTSD clusters were entered into a regression model with the NSI total score as the dependent variable, only the hyperarousal cluster was significantly and positively associated with higher postconcussive symptoms (β=0.46, p=0.005) (Table 3).
Interactions Between TBI Characteristics and PTSD Symptom Clusters on Cognitive Composites and Postconcussive Symptoms
Interaction between blast history and PTSD symptom clusters on cognitive composites.
Because blast history was associated with poorer processing speed performance, four interaction terms were created (blast history-by-re-experiencing, blast history-by-avoidance, blast history-by-hyperarousal, and blast history-by-numbing) to determine whether relationships between PTSD symptom clusters and cognition were moderated by blast-related mTBI. Each of these interaction terms was entered into separate regressions with the corresponding PTSD cluster score and the dichotomous blast-related mTBI variable. As shown in Figure 1, the only significant interaction that emerged was between a history of blast-related mTBI and re-experiencing symptoms (b=−1.182, p=0.025): veterans with a history of blast-related mTBI demonstrated a pattern of worse processing speed associated with higher re-experiencing symptoms (b=−0.058, 95% CI=−0.119, 0.003, t=−1.91, p=0.060), whereas veterans without a history of blast-related mTBI did not demonstrate a significant association between processing speed and re-experiencing symptoms (b=0.052, 95% CI=−0.022, 0.125, t=1.41, p=0.164).
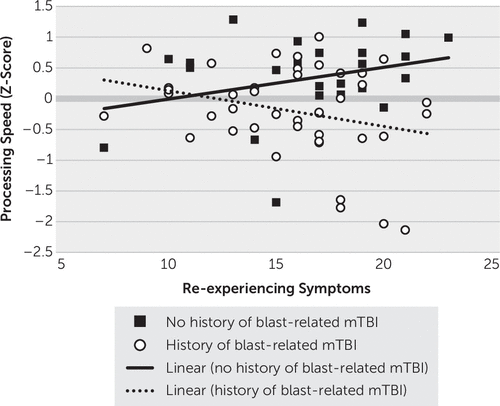
FIGURE 1. Interaction of blast-related mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) history and re-experiencing symptoms on processing speed among Iraq and Afghanistan veterans
Interactions between hyperarousal and TBI characteristics on cognitive composites.
Because hyperarousal was associated with the executive functioning cognitive composite, two interaction terms were created with hyperarousal and the dichotomous TBI characteristics (hyperarousal-by-blast history and hyperarousal-by-number of lifetime mTBIs) to determine whether TBI characteristics moderated the association between hyperarousal symptoms and cognitive performance. Each interaction term was then entered into regression models separately, with the interaction term, hyperarousal cluster scores, and the corresponding TBI characteristic (history of blast-related mTBI, lifetime number of mTBIs) in each model. The only significant interaction that emerged was between lifetime number of mTBIs and hyperarousal symptoms with regard to the processing speed composite (b=−1.54, p=0.009). As shown in Figure 2, veterans with a history of three or more lifetime mTBIs demonstrated worse processing speed associated with higher hyperarousal symptoms (b=−0.079, 95% CI=−0.140, −0.017, t=−2.55, p=0.013), whereas veterans with a history of fewer than three TBIs did not demonstrate a significant association between processing speed and hyperarousal symptoms (b=0.040, 95% CI=−0.023, 0.103, t=1.28, p=0.204).
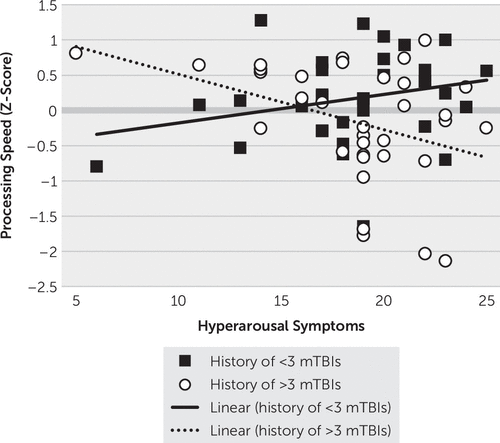
FIGURE 2. Interaction of the number of mild traumatic brain injuries (mTBIs) and hyperarousal symptoms on processing speed among Iraq and Afghanistan veterans
Interactions between hyperarousal and TBI characteristics on postconcussive symptoms.
Because hyperarousal was associated with postconcussive symptoms, the two interaction terms (hyperarousal-by-blast history and hyperarousal-by-number of lifetime mTBIs) were entered into regression models separately, with the interaction term, hyperarousal cluster scores, and the corresponding TBI characteristic (history of blast-related mTBI, lifetime number of mTBIs) in each model to determine whether TBI characteristics moderated the association between hyperarousal symptoms and postconcussive symptoms. There were no significant interactions between TBI characteristics and hyperarousal symptoms with regard to postconcussive symptoms (all p values >0.05).
Discussion
The objective of the present study was to evaluate independent and synergistic associations between PTSD symptom clusters and TBI characteristics on self-reported postconcussive symptoms and objective cognition among treatment-seeking Iraq and Afghanistan veterans with PTSD and a history of mTBI. Higher PTSD symptoms, particularly hyperarousal, were associated with poorer executive functioning and higher postconcussive symptoms. Furthermore, TBI characteristics (mechanism of injury and lifetime number of mTBIs) moderated relationships between processing speed and PTSD symptom clusters of re-experiencing and hyperarousal, such that for those with blast-related or repetitive mTBI, greater re-experiencing and hyperarousal symptoms, respectively, were associated with reduced performance on objective tests of processing speed.
The observed associations between PTSD symptoms and objective cognition are consistent with a large body of literature in civilians and veterans suggesting enduring cognitive compromise associated with psychiatric symptoms in those with a history of mTBI (80–82), particularly on tasks of switching and attention/working memory among those with PTSD (41, 48, 51, 83). With regard to specific PTSD symptom clusters, direct associations were identified between hyperarousal and both executive functioning and self-reported postconcussive symptoms. Additionally, for those with greater injury burden (blast and repetitive mTBI), re-experiencing and hyperarousal symptoms were associated with reduced speed of processing. These results were somewhat consistent with the findings of Swick et al. (52), in which PTSD symptom clusters were associated with executive functioning, although they found that executive dysfunction was most strongly associated with re-experiencing symptoms rather than hyperarousal. The present findings were contrary to those of Aase et al. (21), in which worse verbal learning was associated with greater avoidance and numbing. Various methodological factors (e.g., use of a single measure within a cognitive domain, lack of performance validity measures, differing models of PTSD factors, inclusion of those without a history of mTBI, without PTSD, or subthreshold PTSD) may account for the discrepant findings.
The mechanisms underlying these relationships (hyperarousal symptoms and executive functioning and processing speed, re-experiencing symptoms and processing speed) may be related to difficulty efficiently shifting attention in PTSD (84–86). With regard to hyperarousal, difficulty controlling and shifting attention away from trauma-related associations could hinder the ability to contextualize stimuli, thus leading to exaggerated responses even in safe contexts (87). Difficulties with these functions, as well as the speed with which these processes can take place, may affect the ability to effectively manage emotional and physiological reactions to triggers even loosely related to the trauma memory (88). It is likely that the relationship between cognition and psychological distress is bidirectional (89), in which symptoms of PTSD such as hyperarousal also hinder the ability to perform well on both neuropsychological tests and cognitive tasks required in everyday life.
The results of our study do not support any independent associations between TBI characteristics and objective cognitive functioning. However, TBI characteristics (history of blast or repetitive mTBI) conferred additional risk for poorer processing speed in the presence of higher re-experiencing and hyperarousal symptoms. This finding is somewhat consistent with a retrospective record review study demonstrating slower reaction time and higher PTSD symptoms in Army service members with multiple blast mTBIs (90). The mechanisms underlying the interactions between TBI characteristics and PTSD symptom clusters on processing speed in the present study are not entirely clear; however, it is possible that neurocognitive inefficiencies that are present acutely after mTBI may affect the development and course of PTSD (36, 91, 92) and/or that neurobiological alterations associated with PTSD may cause any neurocognitive inefficiencies to persist (93, 94). Furthermore, associations between re-experiencing symptoms and weakened resting-state connectivity in frontolimbic systems (95), as well as reductions in white matter integrity underlying these connections (96, 97), suggest that a history of mTBI may disrupt the network responsible for protecting trauma associations from entering working memory.
Porter et al. (22) also found postconcussive symptoms were positively related to hyperarousal but not history of mTBI. This association was present even when postconcussive symptoms overlapping with PTSD and depression were removed. Prior research on the convergence between objective and subjective cognitive performance has been equivocal (98). However, in the present study, those with greater hyperarousal demonstrated worse objective cognitive performance and subjective complaints, suggesting that veterans with executive dysfunction may experience more interruption in their daily functioning. Furthermore, they may be more aware of and likely to report these difficulties, which may in turn produce even more distress and associated physiological reactivity. Thus, veterans reporting high postconcussive symptoms as well as high hyperarousal symptoms may also be experiencing objective executive functioning difficulties and therefore may benefit from comprehensive neuropsychological testing or augmented interventions to compensate for their cognitive difficulties.
Although this study has notable strengths, there are also several limitations that must be acknowledged. First, the sample was small, and analyses should be replicated in larger samples. Next, data were cross-sectional and thus it is unknown whether deficits in cognition predate and/or exacerbate PTSD symptoms or vice versa. We also did not have a group with PTSD but without a history of mTBI to determine whether mTBI history exerts effects on PTSD symptom clusters over and above what is observed in PTSD alone. Future research would benefit from inclusion of a relevant, treatment-seeking, PTSD-only group for comparison. However, given diversity within the mTBI sample (mechanism and number of injuries), as well as the treatment-seeking nature of the sample, the present study has implications for treatment (discussed further below). Commonly co-occurring conditions such as depression, pain, and sleep were not assessed using a diagnostic interview and are important variables to include in future research on this population. Another limitation was that a self-report measure was primarily used to assess PTSD symptoms; however, self-report measures have been shown to have high correspondence with clinician-administered measures (99, 100), and this approach has been used previously (27, 59). Finally, the DSM-IV PTSD criteria were used in the present study rather than the updated DSM-5 criteria. Given that many longitudinal studies will likely continue to collect DSM-IV PTSD data, and that the PTSD DSM-IV symptom clusters are still present in DSM-5 (101), the present study provides relevant information on how these symptom clusters relate to important variables in those with PTSD and a history of mTBI.
The specific relationships between re-experiencing and hyperarousal symptoms of PTSD and cognition and self-reported postconcussive symptoms have implications for treatment of those with PTSD and a history of mTBI, especially given that pretreatment characteristics such as cognitive performance, PTSD symptoms, and mechanism of injury have been shown to predict treatment retention and response in veterans with PTSD and/or a history of mTBI (26, 27, 102). The findings from the present study indicate that those with greater mTBI injury burden exhibit associations between slowed processing and higher re-experiencing and hyperarousal symptoms and suggest that treatment should more directly target these symptoms. For example, cognitive rehabilitation before or concurrently with PTSD treatment holds promise to boost treatment compliance and gains in those with comorbid PTSD and mTBI history (27, 59). It may also be of benefit to clinical providers to understand that these cognitive difficulties may play a role in the maintenance of re-experiencing and hyperarousal symptoms or vice versa, particularly if they are refractory to treatment. This may be especially relevant for veterans presenting with subtle processing speed or executive functioning difficulties with a history of blast or repetitive mTBI. Finally, a recent study demonstrated that PTSD moderated the interaction between a history of a single mTBI and executive dysfunction in late middle-aged Vietnam-era male veterans, suggesting that the synergistic association between these variables may continue to be important as Iraq and Afghanistan veterans age (103). Taken together, our findings suggest that ongoing evaluation of the independent and synergistic influences of TBI characteristics and PTSD symptom clusters on cognition and postconcussive symptoms among veterans across the lifespan is warranted.
1 : Assessment of co-occurring disorders in veterans diagnosed with traumatic brain injury . J Head Trauma Rehabil 2012 ; 27 : 253 – 260 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
2 : Neuropsychiatric complications of traumatic brain injury . J Psychosoc Nurs Ment Health Serv 2011 ; 49 : 42 – 50 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
3 : Understanding sequelae of injury mechanisms and mild traumatic brain injury incurred during the conflicts in Iraq and Afghanistan: persistent postconcussive symptoms and posttraumatic stress disorder . Am J Epidemiol 2008 ; 167 : 1446 – 1452 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
4 : Invisible Wounds of War: Psychological and Cognitive Injuries, Their Consequences, and Services to Assist Recovery . Santa Monica, Calif , Rand Corporation , 2008 Google Scholar
5 : The prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder in Operation Enduring Freedom/Operation Iraqi Freedom (OEF/OIF) veterans: a meta-analysis . J Anxiety Disord 2015 ; 31 : 98 – 107 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
6 : Neuropsychological processes in post-traumatic stress disorder . Psychiatr Clin North Am 2002 ; 25 : 295 – 315, vi Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
7 : Prevalence of a positive screen for PTSD among OEF/OIF and OEF/OIF-era veterans in a large population-based cohort . J Trauma Stress 2014 ; 27 : 542 – 549 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
8 : Prevalence of chronic pain, posttraumatic stress disorder, and persistent postconcussive symptoms in OIF/OEF veterans: polytrauma clinical triad . J Rehabil Res Dev 2009 ; 46 : 697 – 702 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
9 : Longitudinal assessment of mental health problems among active and reserve component soldiers returning from the Iraq war . JAMA 2007 ; 298 : 2141 – 2148 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
10 : PTSD and TBI co-morbidity: scope, clinical presentation and treatment options . Brain Inj 2014 ; 28 : 261 – 270 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
11 : The neuropsychological impact of sports-related concussion: a meta-analysis . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2005 ; 11 : 345 – 357 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
12 : Mild Traumatic Brain Injury and Postconcussion Syndrome . New York , Oxford University Press , 2008 Google Scholar
13 : Long-term neuropsychological outcomes following mild traumatic brain injury . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2005 ; 11 : 228 – 236 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
14 : Factors moderating neuropsychological outcomes following mild traumatic brain injury: a meta-analysis . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2005 ; 11 : 215 – 227 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
15 : Summary of the findings of the International Collaboration on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Prognosis . Chiropr Man Therap 2014 ; 22 : 38 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
16 : Prognosis for mild traumatic brain injury: results of the WHO Collaborating Centre Task Force on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury . J Rehabil Med 2004 ; 36 ( Suppl ): 84 – 105 Crossref, Google Scholar
17 : Deployment-related psychiatric and behavioral conditions and their association with functional disability in OEF/OIF/OND veterans . J Trauma Stress 2015 ; 28 : 25 – 33 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
18 : Prospectively assessed clinical outcomes in concussive blast vs nonblast traumatic brain injury among evacuated US military personnel . JAMA Neurol 2014 ; 71 : 994 – 1002 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
19 : The impact of multiple concussions on emotional distress, post-concussive symptoms, and neurocognitive functioning in active duty United States marines independent of combat exposure or emotional distress . J Neurotrauma 2014 ; 31 : 1823 – 1834 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
20 : Mild traumatic brain injury (concussion), posttraumatic stress disorder, and depression in U.S. soldiers involved in combat deployments: association with postdeployment symptoms . Psychosom Med 2012 ; 74 : 249 – 257 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
21 : PTSD symptoms are associated with visual retrieval performance in OEF/OIF/OND veterans . Psychiatry Res 2017 ; 257 : 156 – 162 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
22 : Postconcussive symptoms (PCS) following combat-related traumatic brain injury (TBI) in Veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD): Influence of TBI, PTSD, and depression on symptoms measured by the Neurobehavioral Symptom Inventory (NSI) . J Psychiatr Res 2018 ; 102 : 8 – 13 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
23 : Repetitive traumatic brain injury, psychological symptoms, and suicide risk in a clinical sample of deployed military personnel . JAMA Psychiatry 2013 ; 70 : 686 – 691 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
24 : Mild traumatic brain injury burden moderates the relationship between cognitive functioning and suicidality in Iraq/Afghanistan-Era veterans . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2019 ; 25 : 79 – 89 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
25 : Chronic postconcussion symptoms and functional outcomes in OEF/OIF veterans with self-report of blast exposure . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2013 ; 19 : 1 – 10 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
26 : Neurocognitive correlates of successful treatment of PTSD in female veterans . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2016 ; 22 : 643 – 651 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
27 : Worse baseline executive functioning is associated with dropout and poorer response to trauma-focused treatment for veterans with PTSD and comorbid traumatic brain injury . Behav Res Ther 2018 ; 108 : 68 – 77 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
28 : Multiple past concussions are associated with ongoing post-concussive symptoms but not cognitive impairment in active-duty army soldiers . J Neurotrauma 2015 ; 32 : 1301 – 1306 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
29 : A multisite study of the relationships between blast exposures and symptom reporting in a post-deployment active duty military population with mild traumatic brain injury . J Neurotrauma 2014 ; 31 : 1899 – 1906 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
30 : Repetitive mild traumatic brain injury in military veterans is associated with increased neuropsychological intra-individual variability . Neuropsychologia 2018 ; 119 : 340 – 348 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
31 : Neuropsychological performance and subjective symptom reporting in military service members with a history of multiple concussions: Comparison with a single concussion, posttraumatic stress disorder, and orthopedic trauma . J Head Trauma Rehabil 2018 ; 33 : 81 – 90 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
32 : Cognitive sequelae of blast-related versus other mechanisms of brain trauma . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2009 ; 15 : 1 – 8 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
33 Prevalence and Epidemiology of Combat Blast Injuries From the Military Cohort 2001-2014. Washington, DC, Department of Veterans Affairs, 2016 Google Scholar
34 : Neuropsychological outcome from blast versus non-blast: mild traumatic brain injury in US military service members . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2012 ; 18 : 595 – 605 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
35 : Postconcussive symptoms after blast and nonblast-related mild traumatic brain injuries in Afghanistan and Iraq war veterans . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2010 ; 16 : 856 – 866 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
36 : Comparison of concussive symptoms, cognitive performance, and psychological symptoms between acute blast-versus nonblast-induced mild traumatic brain injury . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2011 ; 17 : 36 – 45 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
37 : Mild traumatic brain injury (concussion) during combat: lack of association of blast mechanism with persistent postconcussive symptoms . J Head Trauma Rehabil 2010 ; 25 : 9 – 14 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
38 : Verbal memory deficits in OEF/OIF/OND veterans exposed to blasts at close range . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2018 ; 24 : 466 – 475 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
39 : Blast-related mild traumatic brain injury: a Bayesian random-effects meta-analysis on the cognitive outcomes of concussion among military personnel . Neuropsychol Rev 2014 ; 24 : 428 – 444 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
40 : Comparing the neuropsychological test performance of Operation Enduring Freedom/Operation Iraqi Freedom (OEF/OIF) veterans with and without blast exposure, mild traumatic brain injury, and posttraumatic stress symptoms . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2015 ; 21 : 353 – 363 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
41 : A quantitative meta-analysis of neurocognitive functioning in posttraumatic stress disorder . Psychol Bull 2015 ; 141 : 105 – 140 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
42 : Comprehensive analysis of the predictors of neurobehavioral symptom reporting in veterans . Neurology 2018 ; 91 : e732 – e745 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
43 : Clinically significant cognitive dysfunction in OEF/OIF/OND veterans: prevalence and clinical associations . Neuropsychology 2019 ; 33 : 534 – 546 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
44 : Elevated rates of memory impairment in military service-members and veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder . J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 2017 ; 39 : 768 – 785 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
45 : Posttraumatic psychological symptoms are associated with reduced inhibitory control, not general executive dysfunction . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2015 ; 21 : 342 – 352 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
46 : Trauma-related psychiatric and behavioral conditions are uniquely associated with sustained attention dysfunction . Neuropsychology 2019 ; 33 : 711 – 724 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
47 : The effects of mild traumatic brain injury, post-traumatic stress disorder, and combined mild traumatic brain injury/post-traumatic stress disorder on returning veterans . J Neurotrauma 2015 ; 32 : 956 – 966 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
48 : Neuropsychological effects of self-reported deployment-related mild TBI and current PTSD in OIF/OEF veterans . Clin Neuropsychol 2013 ; 27 : 881 – 907 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
49 : PTSD modifies performance on a task of affective executive control among deployed OEF/OIF veterans with mild traumatic brain injury . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2013 ; 19 : 792 – 801 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
50 : Neurobiological indicators of disinhibition in posttraumatic stress disorder . Hum Brain Mapp 2015 ; 36 : 3076 – 3086 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
51 : Neuropsychological functioning in veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder: associations with performance validity, comorbidities, and functional outcomes . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2016 ; 22 : 399 – 411 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
52 : Impaired response inhibition in veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder and mild traumatic brain injury . J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2012 ; 18 : 917 – 926 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
53 : Evaluation of a hybrid treatment for veterans with comorbid traumatic brain injury and posttraumatic stress disorder: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial . Contemp Clin Trials 2015 ; 45 ( Pt B ): 210 – 216 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
54 : Validity testing and neuropsychology practice in the VA healthcare system: results from recent practitioner survey . Clin Neuropsychol 2016 ; 30 : 497 – 514 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
55 : Confirmatory factor analysis of the clinician-administered PTSD Scale: evidence for the dimensionality of posttraumatic stress disorder . Psychol Assess 1998 ; 10 : 90 – 96 Crossref, Google Scholar
56 : Latent factor structure of PTSD symptoms in veterans with a history of mild traumatic brain injury and close-range blast exposure . (Epub ahead of print, ahead of print, 2018) Psychol Trauma 2019 ; 11 : 442 – 450 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
57 : Reporting of symptoms associated with concussion by OEF/OIF/OND veterans: comparison between research and clinical contexts . Brain Inj 2017 ; 31 : 485 – 492 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
58 : Poor performance validity predicts clinical characteristics and cognitive test performance of OEF/OIF/OND veterans in a research setting . Clin Neuropsychol 2014 ; 28 : 802 – 825 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
59 : SMART-CPT treatment for veterans with comorbid post-traumatic stress disorder and history of traumatic brain injury: a randomised controlled trial . J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2019 ; 90 : 333 – 341 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
60 : VA/DoD clinical practice guideline for management of concussion-mild traumatic brain injury. Washington, DC Department of Veterans Affairs, 2016 Google Scholar
61 : VA/DOD clinical practice guideline for management of concussion/mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) . J Rehabil Res Dev 2009 ; 46 : CP1 – CP68 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
62 : Mild traumatic brain injury characteristics do not negatively influence cognitive processing therapy attendance or outcomes . J Psychiatr Res 2019 ; 116 : 7 – 13 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
63 American Psychiatric Association : Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, Text Revision . Washington, DC , , 2000 Crossref, Google Scholar
64 : Wide Range Achievement Test , 4th ed . Torrence, Calif , Western Psychological Services , 2006 Google Scholar
65 : Clinical utility of the mBIAS and NSI validity-10 to detect symptom over-reporting following mild TBI: A multicenter investigation with military service members . J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 2018 ; 40 : 213 – 223 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
66 : Persistent postconcussion syndrome: the structure of subjective complaints after mild traumatic brain injury . J Head Trauma Rehabil 1995 ; 10 : 1 – 17 Crossref, Google Scholar
67 : Traumatic brain injury screening: preliminary findings in a US Army Brigade Combat Team . J Head Trauma Rehabil 2009 ; 24 : 14 – 23 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
68 Weathers F, Litz B, Herman D, et al: The PTSD Checklist (PCL): Reliability, validity, and diagnostic utility, proceedings presented at the annual convention of the International Society for Traumatic Stress Studies, 1993, San Antonio, TexGoogle Scholar
69 : Dimensionality of posttraumatic stress symptoms: a confirmatory factor analysis of DSM-IV symptom clusters and other symptom models . Behav Res Ther 2000 ; 38 : 203 – 214 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
70 : Synthesis of the psychometric properties of the PTSD checklist (PCL) military, civilian, and specific versions . Depress Anxiety 2011 ; 28 : 596 – 606 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
71 : Test of Memory Malingering . New York , Multi-Health Systems , 1996 Google Scholar
72 : The California Verbal Learning Test , 2nd ed . San Antonio, Tex , Psychological Corporation , 2000 Google Scholar
73 : The dangers of failing one or more performance validity tests in individuals claiming mild traumatic brain injury-related postconcussive symptoms . Arch Clin Neuropsychol 2014 ; 29 : 614 – 624 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
74 : Neuropsychological assessment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) ; in Handbook of Medical Neuropsychology . Edited by Armstrong C , Morrow L . New York, Springer , 2010 , pp 447 – 465 Crossref, Google Scholar
75 : Recommendations for the use of common outcome measures in traumatic brain injury research . Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2010 ; 91 : 1650 – 1660.e17 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
76 : Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale , 4th ed . San Antonio, Tex , Psychological Corporation , 2008 Google Scholar
77 : Delis-Kaplan Executive Function System (DKEFS) . San Antonio, Tex , Psychological Corporation , 2001 Google Scholar
78 : Wisconsin Card Sorting Test-64 Card Version (WCST-64) . Odessa, FL , Psychological Assessment Resources , 2000 Google Scholar
79 : No adjustments are needed for multiple comparisons . Epidemiology 1990 ; 1 : 43 – 46 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
80 : The prospective course of postconcussion syndrome: the role of mild traumatic brain injury . Neuropsychology 2011 ; 25 : 454 – 465 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
81 : Longitudinal effects of mild traumatic brain injury and posttraumatic stress disorder comorbidity on postdeployment outcomes in national guard soldiers deployed to Iraq . Arch Gen Psychiatry 2011 ; 68 : 79 – 89 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
82 Vasterling JJ , Bryant RA , Keane TM (eds): PTSD and Mild Traumatic Brain Injury . New York , Guilford Pres , 2012 Google Scholar
83 : A meta-analysis of the relationship between symptom severity of posttraumatic stress disorder and executive function . Cogn Neuropsychiatry 2017 ; 22 : 1 – 16 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
84 : The role of trauma-related distractors on neural systems for working memory and emotion processing in posttraumatic stress disorder . J Psychiatr Res 2009 ; 43 : 809 – 817 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
85 : Combat veterans with comorbid PTSD and mild TBI exhibit a greater inhibitory processing ERP from the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex . Psychiatry Res 2014 ; 224 : 58 – 66 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
86 : Attention and memory dysfunction in posttraumatic stress disorder . Neuropsychology 1998 ; 12 : 125 – 133 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
87 : Executive function and PTSD: disengaging from trauma . Neuropharmacology 2012 ; 62 : 686 – 694 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
88 : Memory in PTSD: A neurocognitive approach ; in Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder . Edited by LeDoux J , Keane T , Shiromani P . New York , Humana Press , 2009 , pp 105 – 130 Crossref, Google Scholar
89 : Relationships among cognition, emotion, and motivation: implications for intervention and neuroplasticity in psychopathology . Front Hum Neurosci 2013 ; 7 : 261 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
90 : Residual effects of combat-related mild traumatic brain injury . J Neurotrauma 2013 ; 30 : 680 – 686 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
91 : Factors influencing cognitive functioning following mild traumatic brain injury in OIF/OEF burn patients . NeuroRehabilitation 2010 ; 26 : 233 – 238 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
92 : Concussion alters the functional brain processes of visual attention and working memory . J Neurotrauma 2018 ; 35 : 267 – 277 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
93 : The nature of white matter abnormalities in blast-related mild traumatic brain injury . Neuroimage Clin 2015 ; 8 : 148 – 156 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
94 : Neuropsychological outcomes in OEF/OIF veterans with self-report of blast exposure: associations with mental health, but not MTBI . Neuropsychology 2014 ; 28 : 337 – 346 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
95 : Brain network disturbance related to posttraumatic stress and traumatic brain injury in veterans . Biol Psychiatry 2015 ; 78 : 210 – 216 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
96 : Connecting combat-related mild traumatic brain injury with posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms through brain imaging . Neurosci Lett 2014 ; 577 : 11 – 15 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
97 : Decreases in white matter integrity of ventro-limbic pathway linked to post-traumatic stress disorder in mild traumatic brain injury . J Neurotrauma 2019 ; 36 : 1093 – 1098 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
98 : Are self-reported symptoms of executive dysfunction associated with objective executive function performance following mild to moderate traumatic brain injury? J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 2011 ; 33 : 704 – 714 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
99 : Validating the primary care posttraumatic stress disorder screen and the posttraumatic stress disorder checklist with soldiers returning from combat . J Consult Clin Psychol 2008 ; 76 : 272 – 281 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
100 : Change in posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms: do clinicians and patients agree? Psychol Assess 2008 ; 20 : 131 – 138 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
101 American Psychiatric Association : Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , 5th ed . Washington, DC , , 2013 Crossref, Google Scholar
102 : Multidisciplinary treatment of patients with persistent post concussive complaints significantly reduces symptom burden . J Head Trauma Rehabil 2015 ; 32(1): 1 Crossref, Google Scholar
103 : Interactive effect of traumatic brain injury and psychiatric symptoms on cognition among late middle-aged men: findings from the Vietnam Era Twin Study of Aging . J Neurotrauma 2019 ; 36 : 338 – 347 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar



